As the world transitions from carbon-based sources of energy to a more sustainable future, demand is increasing for a range of minerals and metals required for the transition to cleaner sources of energy. From uses in home appliances, transportation, construction, electrical components, and medicine to aerospace technology and infrastructure development, minerals are essential components of modern life. In addition to these applications, minerals such as copper, nickel, platinum, silver, gold, aluminium, cobalt, and lithium are used in renewable energy technologies like batteries for electricity storage, wind turbines, and photovoltaic cells for harnessing energy from the sun.
Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG7), which calls for “affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all,” aims to increase the share of renewables in the global energy mix and ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and clean energy. The decarbonizing technologies required to transition to wind, solar, batteries, and other sustainable energy sources are driving increased demand for these scarce natural resources, creating significant economic opportunities for countries where the minerals are found but also posing social and environmental risks.
Risks Associated with Mineral Mining
While minerals are essential for the transition to an electrified future, their extraction from the ground creates a range of social and environmental challenges in countries where the minerals are mined. Extractive industries pose risks to human health, water supplies, and ecosystems. Mining can ravage landscapes, decimate biodiversity, lead to human rights abuses, and be a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions as well.
Other risks include deforestation, soil erosion, water contamination, dust, and noise pollution. Land-based mining is encroaching on wildlife areas and accelerating the rates of extinction of endangered plant and animal species. The extensive land required for mining is also impacting indigenous populations and leading to a crisis of pollution and toxic waste in local communities.
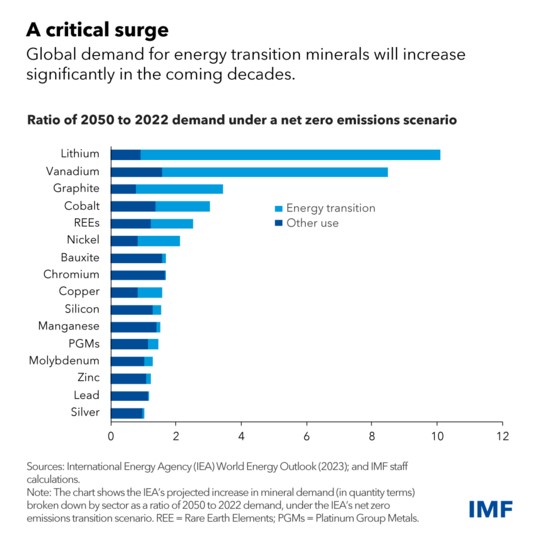
Economic Opportunities for African Countries
With growing demand, proceeds from critical minerals are poised to rise significantly over the next two decades. Global revenues from the extraction of just four key minerals—copper, nickel, cobalt, and lithium—are estimated to total $16 trillion over the next 25 years, in 2023-dollar terms, says the IMF. With sub-Saharan Africa estimated to hold about 30 percent of the volume of proven critical mineral reserves needed to power the transition to renewable energies, this means that Africa stands to reap over 10 percent of these cumulated revenues, which could correspond to an increase in the region’s GDP by 12 percent or more by 2050, according to the IMF.
The Canadian Mining Journal on Africa’s mining potential reports that the extraction and export of these mineral resources contribute significantly to national revenues, foreign currency reserves, and employment. Lithium, cobalt, copper, manganese, graphite, and many other critical minerals are abundant in the region. Africa produces over 60 metal and mineral products and has huge potential for mineral reserve exploration and production. Over 30% of the world’s mineral reserves are found in Africa, with practically every country on the continent producing at least one critical mineral. According to the Policy Centre for the New South’s research on Africa’s mining potential, sub-Saharan Africa accounts for around 80% of global platinum production, 50% of manganese, two-thirds of cobalt, and a considerable proportion of chromium.
In spite of the abundance of raw materials, many African countries still export most of the mineral resources in their raw forms. Approximately 70% of mined minerals are exported to Europe or Asia for refining. This shows that local processing options for critical minerals are still limited.

Since the bulk of the economic benefit from these minerals is derived from the refining of the raw materials, the greatest economic gains are realized elsewhere. Developing local processing industries could significantly create higher-skilled jobs and increase tax revenues, thereby supporting poverty reduction and sustainable development. Africa can generate even greater windfalls by not only exporting raw materials but processing them as well. Raw bauxite, for instance, fetches a modest $65 per ton, but when processed into aluminium, it commands a hefty $2,335 per ton in end-2023 prices according to the IMF.
In line with this, many governments on the continent are undertaking structural reforms to support domestic companies in mining and related processing sectors to retain greater economic value onshore. This includes implementing policies aimed at restricting the exports of raw mineral resources. For instance, Ghana has implemented a green minerals policy aimed at retaining a greater portion of the value chain from the country’s natural resources. Namibia and Zimbabwe have taken similar steps regarding the export of unprocessed lithium.

Realizing the Gains While Minimising the Risks
If managed properly, the extraction of these critical minerals has the potential to transform the region’s economic status, according to IMF’s latest Regional Economic Outlook. Accessing these critical minerals in ways that minimize the impact on local communities, protect biodiversity, respect the land rights of indigenous communities, protect workers, and reduce the environmental impacts on surrounding ecosystems is essential if we are to create a sustainable future for everyone. Massive wealth transfers of raw materials in ways that negatively impact communities in the global south to the benefit of consuming economies in the global north are not the answer to a sustainable future.